Back
Anatomy
Back
Facts
Back Anatomy
Causes of Low Back Pain
Testing
Treatment Options
The spinal column (or vertebral column) extends
from the skull to the pelvis and is made up of 33 individual
bones termed vertebrae. The vertebrae are stacked on top of
each other group into four regions:
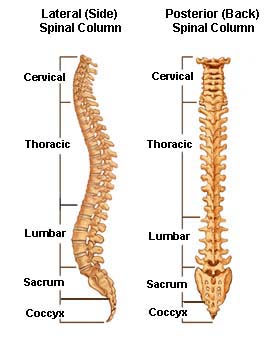
| Term |
#
of Vertebrae
|
Body
Area |
Abbreviation |
| Cervical |
7 |
Neck |
C1 – C7 |
| Thoracic |
12 |
Chest |
T1 – T12 |
| Lumbar |
5
or 6 |
Low
Back |
L1 – L5 |
| Sacrum |
5
(fused) |
Pelvis |
S1 – S5 |
| Coccyx |
3 |
Tailbone |
None |
The
cervical spine is further divided into two parts; the upper
cervical region (C1 and C2), and the lower cervical region
(C3 through C7). C1 is termed the Atlas and C2 the Axis.
The Occiput (CO), also known as the Occipital Bone,
is a flat bone that forms the back of the head.
Atlas (C1)
The
Atlas is the first cervical vertebra and therefore abbreviated
C1. This vertebra supports the skull. Its appearance is different
from the other spinal vertebrae. The atlas is a ring of bone
made up of two lateral masses joined at the front and back
by the anterior arch and the posterior arch.
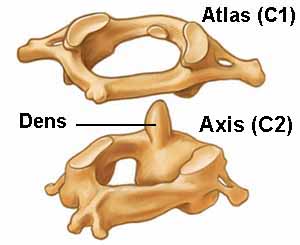
Axis
(C2)
The Axis is the second cervical vertebra or C2. It is a blunt tooth–like
process that projects upward. It is also referred to as the ‘dens’ (Latin
for ‘tooth’) or odontoid process. The dens provides a type of pivot
and collar allowing the head and atlas to rotate around the dens.
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1 – T12)
The thoracic vertebrae increase in size from T1 through T12. They are characterized
by small pedicles, long spinous processes, and relatively large intervertebral
foramen (neural passageways), which result in less incidence of nerve compression.
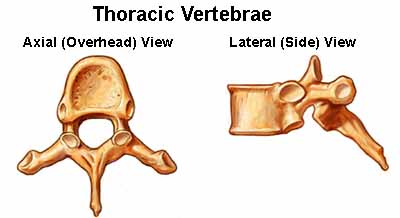
The
rib cage is joined to the thoracic vertebrae. At T11 and
T12, the ribs do not attach and are so are called "floating
ribs." The thoracic spine's range of motion is limited due
to the many rib/vertebrae connections and the long spinous
processes.

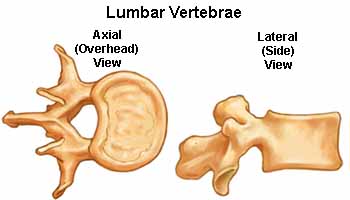
Lumbar
Vertebrae (L1 – L5)
The lumbar vertebrae graduate in size from L1 through L5. These vertebrae bear
much of the body's weight and related biomechanical stress. The pedicles are
longer and wider than those in the thoracic spine. The spinous processes are
horizontal and more squared in shape. The intervertebral foramen (neural passageways)
are relatively large but nerve root compression is more common than in the
thoracic spine.
Continued
Salama
Chiropractic Center
Wendover Chiropractic Clinic Location
Suite
A, 3410 West
Wendover Avenue• Greensboro, North Carolina 27407
© 2006 All Rights Reserved.
|





